有时候,我们需要知道从哪开始有了分支和标签,同时想知道这条支路是单独的分支还是树型结构。如果需要你可以使用 → 。
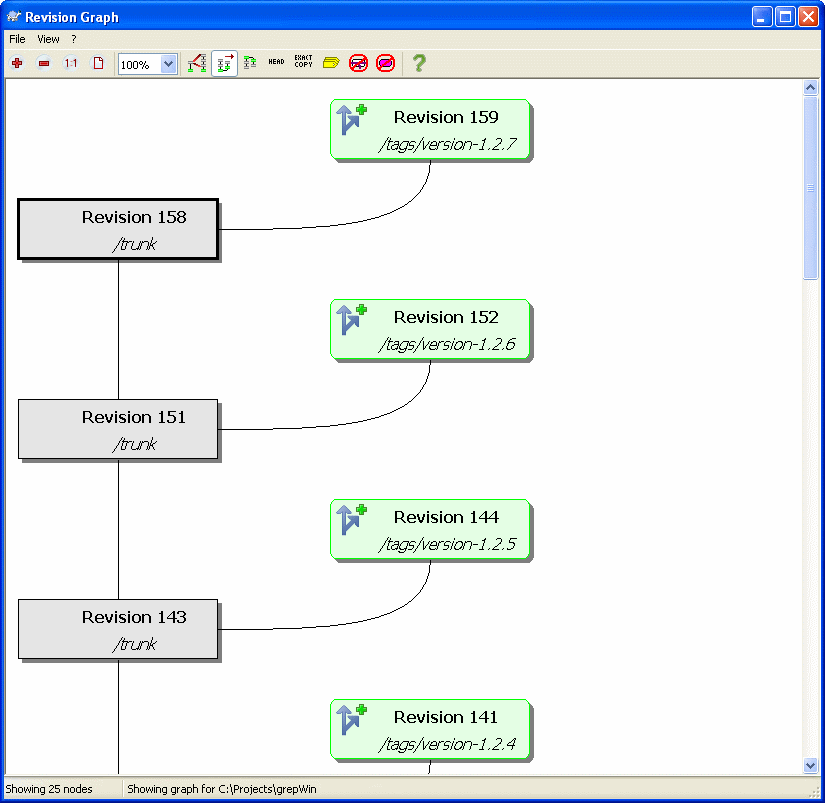
这个版本历史分析图能够显示分支/标签从什么地方开始创建,以及什么时候删除。
重要
In order to generate the graph, TortoiseSVN must fetch all log messages from the repository root. Needless to say this can take several minutes even with a repository of a few thousand revisions, depending on server speed, network bandwidth, etc. If you try this with something like the Apache project which currently has over 500,000 revisions you could be waiting for some time.
The good news is that if you are using Log Caching, you only have to suffer this delay once. After that, log data is held locally. Log caching is enabled in TortoiseSVN's settings.
The revision graph shows several types of node:
- 增加文件/文件夹
已增加或通过复制生成的文件/文件夹以圆圈的方式标记。
- 已删除文件/文件夹
已删除文件,比如说一个不在需要的分支,将显示octagon(rectangle with corners cut off)。
- 分支最新版本
Where a branch (or trunk or tag) has been modified since the last branch node, this is shown using an ellipse. Shown when the Show HEAD revisions option is selected.
- 一般的文件/文件夹
其他一般的文件用plain rectangle标示。
Note that by default the graph only shows the points at which items were added or deleted. Showing every revision of a project will generate a very large graph for non-trivial cases. If you really want to see all revisions where changes were made, there is an option to do this in the View menu and on the toolbar.
因为版本图经常很复杂,所以有很多方法剪裁视图。你可以在视图菜单或工具栏找到它们。
- 分组分支
The default behavior (grouping off) will use one row per revision and all rows are sorted strictly by revision. As a result, long-living branches occupy a whole column for only a few changes and the graph becomes very broad.
This mode groups changes by branch, so that there is no global revision ordering: Consecutive revisions on a branch will be shown in (often) consecutive lines. Sub-branches, however, are arranged in such a way that later branches will be shown in the same column above older branches to keep the graph slim. As a result, a given row may contain changes from different revisions.
- 最老的在顶部
正常情况下,在图形底部显示最老的版本,版本树向上生长。使用这个选项,版本树从顶部向下生长。
- 显示最新版本
它确保每个分支的最新版本永远在图中显示。
- 精确复制源
When a branch/tag is made, the default behaviour is to show the branch as taken from the last node where a change was made. Strictly speaking this is inaccurate since the branches are often made from the current HEAD rather than a specific revision. So it is possible to show the more correct (but less useful) revision that was used to create the copy.
- 折叠标签
If you want to see a graph of software development, tagged releases may be of little interest to you. This option hides the nodes for tags and shows them instead in the tooltip for the node that they were copied from. A tag icon on the right side of the source node indicates that tags were made.
- 减少交叉行
如果图形布局产生许多交叉行,可使用这个选项来清理。它可以让布局列在更少的逻辑位置显示,例如使用斜线而不是列,可能需要少许时间来优化显示。
- 过滤器
Sometimes the revision graph contains more revisions than you want to see. This option opens a dialog which allows you to restrict the range of revisions displayed, and to hide particular paths by name.
概览窗口可以使遍历大图更容易。它在小窗口中显示整个图形,高亮显示当前详细显示的部分。你可以通过拖曳高亮区域来改变当前详细显示的部分。
任何时候只要鼠标在版本框上滑过,都会显示该版本的日期、作者和备注信息。
If you select two revisions (Use Ctrl-left click), you can use the context menu to show the differences between these revisions. You can choose to show differences as at the branch creation points, but usually you will want to show the differences at the branch end points, i.e. at the HEAD revision.
你可以用查看单一差异文件的方式来查看差异,它在单一的文件中显示差异。如果你选 → 所有修改过的文件都会呈现在列表中。双击一个文件名可以返回文件版本号和他们差异。
如果右击一个版本你可以使用 → 来查看它的历史。
You can also merge changes in the selected revision(s) into a different working copy. A folder selection dialog allows you to choose the working copy to merge into, but after that there is no confirmation dialog, nor any opportunity to try a dry run. It is a good idea to merge into an unmodified working copy so that you can revert the changes if it doesn't work out! This is a useful feature if you want to merge selected revisions from one branch to another.
小心
因为Subversion不能支持提供所有请求的信息,在有大量请求信息时,有时它能提供强大的返回信息。但无论如何,主干都会产生有用的输出。
If you want to check the server again for newer information, you can simply refresh the view using F5. If you are using the log cache (enabled by default), this will check the repository for newer commits and fetch only the new ones. If the log cache was in offline mode, this will also attempt to go back online.
If you are using the log cache and you think the message content or author may have changed, you should use the log dialog to refresh the messages you need. Since the revision graph works from the repository root, we would have to invalidate the entire log cache, and refilling it could take a very long time.