第16章 设计范式
本章要向大家介绍重要但却并不是那么传统的“范式”(Pattern)程序设计方法。
在向面向对象程序设计的演化过程中,或许最重要的一步就是“设计范式”(Design
Pattern)的问世。它在由Gamma,Helm和Johnson编著的《Design Patterns》一书中被定义成一个“里程碑”(该书由Addison-Wesley于1995年出版,注释①)。那本书列出了解决这个问题的23种不同的方法。在本章中,我们准备伴随几个例子揭示出设计范式的基本概念。这或许能激起您阅读《Design
Pattern》一书的欲望。事实上,那本书现在已成为几乎所有OOP程序员都必备的参考书。
①:但警告大家:书中的例子是用C++写的。
本章的后一部分包含了展示设计进化过程的一个例子,首先是比较原始的方案,经过逐渐发展和改进,慢慢成为更符合逻辑、更为恰当的设计。该程序(仿真垃圾分类)一直都在进化,可将这种进化作为自己设计方案的一个原型——先为特定的问题提出一个适当的方案,再逐步改善,使其成为解决那类问题一种最灵活的方案。
16.1 范式的概念
在最开始,可将范式想象成一种特别聪明、能够自我适应的手法,它可以解决特定类型的问题。也就是说,它类似一些需要全面认识某个问题的人。在了解了问题的方方面面以后,最后提出一套最通用、最灵活的解决方案。具体问题或许是以前见到并解决过的。然而,从前的方案也许并不是最完善的,大家会看到它如何在一个范式里具体表达出来。
尽管我们称之为“设计范式”,但它们实际上并不局限于设计领域。思考“范式”时,应脱离传统意义上分析、设计以及实施的思考方式。相反,“范式”是在一个程序里具体表达一套完整的思想,所以它有时可能出现在分析阶段或者高级设计阶段。这一点是非常有趣的,因为范式具有以代码形式直接实现的形式,所以可能不希望它在低级设计或者具体实施以前显露出来(而且事实上,除非真正进入那些阶段,否则一般意识不到自己需要一个范式来解决问题)。
范式的基本概念亦可看成是程序设计的基本概念:添加一层新的抽象!只要我们抽象了某些东西,就相当于隔离了特定的细节。而且这后面最引人注目的动机就是“将保持不变的东西身上发生的变化孤立出来”。这样做的另一个原因是一旦发现程序的某部分由于这样或那样的原因可能发生变化,我们一般都想防止那些改变在代码内部繁衍出其他变化。这样做不仅可以降低代码的维护代价,也更便于我们理解(结果同样是降低开销)。
为设计出功能强大且易于维护的应用项目,通常最困难的部分就是找出我称之为“领头变化”的东西。这意味着需要找出造成系统改变的最重要的东西,或者换一个角度,找出付出代价最高、开销最大的那一部分。一旦发现了“领头变化”,就可以为自己定下一个焦点,围绕它展开自己的设计。
所以设计范式的最终目标就是将代码中变化的内容隔离开。如果从这个角度观察,就会发现本书实际已采用了一些设计范式。举个例子来说,继承可以想象成一种设计范式(类似一个由编译器实现的)。在都拥有同样接口(即保持不变的东西)的对象内部,它允许我们表达行为上的差异(即发生变化的东西)。合成亦可想象成一种范式,因为它允许我们修改——动态或静态——用于实现类的对象,所以也能修改类的运作方式。
在《Design Patterns》一书中,大家还能看到另一种范式:“继承器”(即Iterator,Java
1.0和1.1不负责任地把它叫作Enumeration,即“枚举”;Java1.2的集合则改回了“继承器”的称呼)。当我们在集合里遍历,逐个选择不同的元素时,继承器可将集合的实施细节有效地隐藏起来。利用继承器,可以编写出通用的代码,以便对一个序列里的所有元素采取某种操作,同时不必关心这个序列是如何构建的。这样一来,我们的通用代码即可伴随任何能产生继承器的集合使用。
16.1.1 单子
或许最简单的设计范式就是“单子”(Singleton),它能提供对象的一个(而且只有一个)实例。单子在Java库中得到了应用,但下面这个例子显得更直接一些:
//: SingletonPattern.java
// The Singleton design pattern: you can
// never instantiate more than one.
package c16;
// Since this isn't inherited from a Cloneable
// base class and cloneability isn't added,
// making it final prevents cloneability from
// being added in any derived classes:
final class Singleton {
private static Singleton s = new Singleton(47);
private int i;
private Singleton(int x) { i = x; }
public static Singleton getHandle() {
return s;
}
public int getValue() { return i; }
public void setValue(int x) { i = x; }
}
public class SingletonPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton s = Singleton.getHandle();
System.out.println(s.getValue());
Singleton s2 = Singleton.getHandle();
s2.setValue(9);
System.out.println(s.getValue());
try {
// Can't do this: compile-time error.
// Singleton s3 = (Singleton)s2.clone();
} catch(Exception e) {}
}
} ///:~//: BoxObserver.java
// Demonstration of Observer pattern using
// Java's built-in observer classes.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
// You must inherit a new type of Observable:
class BoxObservable extends Observable {
public void notifyObservers(Object b) {
// Otherwise it won't propagate changes:
setChanged();
super.notifyObservers(b);
}
}
public class BoxObserver extends Frame {
Observable notifier = new BoxObservable();
public BoxObserver(int grid) {
setTitle("Demonstrates Observer pattern");
setLayout(new GridLayout(grid, grid));
for(int x = 0; x < grid; x++)
for(int y = 0; y < grid; y++)
add(new OCBox(x, y, notifier));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int grid = 8;
if(args.length > 0)
grid = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Frame f = new BoxObserver(grid);
f.setSize(500, 400);
f.setVisible(true);
f.addWindowListener(
new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class OCBox extends Canvas implements Observer {
Observable notifier;
int x, y; // Locations in grid
Color cColor = newColor();
static final Color[] colors = {
Color.black, Color.blue, Color.cyan,
Color.darkGray, Color.gray, Color.green,
Color.lightGray, Color.magenta,
Color.orange, Color.pink, Color.red,
Color.white, Color.yellow
};
static final Color newColor() {
return colors[
(int)(Math.random() * colors.length)
];
}
OCBox(int x, int y, Observable notifier) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
notifier.addObserver(this);
this.notifier = notifier;
addMouseListener(new ML());
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.setColor(cColor);
Dimension s = getSize();
g.fillRect(0, 0, s.width, s.height);
}
class ML extends MouseAdapter {
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
notifier.notifyObservers(OCBox.this);
}
}
public void update(Observable o, Object arg) {
OCBox clicked = (OCBox)arg;
if(nextTo(clicked)) {
cColor = clicked.cColor;
repaint();
}
}
private final boolean nextTo(OCBox b) {
return Math.abs(x - b.x) <= 1 &&
Math.abs(y - b.y) <= 1;
}
} ///:~//: RecycleA.java
// Recycling with RTTI
package c16.recyclea;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
abstract class Trash {
private double weight;
Trash(double wt) { weight = wt; }
abstract double value();
double weight() { return weight; }
// Sums the value of Trash in a bin:
static void sumValue(Vector bin) {
Enumeration e = bin.elements();
double val = 0.0f;
while(e.hasMoreElements()) {
// One kind of RTTI:
// A dynamically-checked cast
Trash t = (Trash)e.nextElement();
// Polymorphism in action:
val += t.weight() * t.value();
System.out.println(
"weight of " +
// Using RTTI to get type
// information about the class:
t.getClass().getName() +
" = " + t.weight());
}
System.out.println("Total value = " + val);
}
}
class Aluminum extends Trash {
static double val = 1.67f;
Aluminum(double wt) { super(wt); }
double value() { return val; }
static void value(double newval) {
val = newval;
}
}
class Paper extends Trash {
static double val = 0.10f;
Paper(double wt) { super(wt); }
double value() { return val; }
static void value(double newval) {
val = newval;
}
}
class Glass extends Trash {
static double val = 0.23f;
Glass(double wt) { super(wt); }
double value() { return val; }
static void value(double newval) {
val = newval;
}
}
public class RecycleA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector bin = new Vector();
// Fill up the Trash bin:
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++)
switch((int)(Math.random() * 3)) {
case 0 :
bin.addElement(new
Aluminum(Math.random() * 100));
break;
case 1 :
bin.addElement(new
Paper(Math.random() * 100));
break;
case 2 :
bin.addElement(new
Glass(Math.random() * 100));
}
Vector
glassBin = new Vector(),
paperBin = new Vector(),
alBin = new Vector();
Enumeration sorter = bin.elements();
// Sort the Trash:
while(sorter.hasMoreElements()) {
Object t = sorter.nextElement();
// RTTI to show class membership:
if(t instanceof Aluminum)
alBin.addElement(t);
if(t instanceof Paper)
paperBin.addElement(t);
if(t instanceof Glass)
glassBin.addElement(t);
}
Trash.sumValue(alBin);
Trash.sumValue(paperBin);
Trash.sumValue(glassBin);
Trash.sumValue(bin);
}
} ///:~ for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++)
switch((int)(Math.random() * 3)) {
case 0 :
bin.addElement(new
Aluminum(Math.random() * 100));
break;
case 1 :
bin.addElement(new
Paper(Math.random() * 100));
break;
case 2 :
bin.addElement(new
Glass(Math.random() * 100));
}class Info {
int type;
// Must change this to add another type:
static final int MAX_NUM = 4;
double data;
Info(int typeNum, double dat) {
type = typeNum % MAX_NUM;
data = dat;
}
} static Trash factory(Info i) {
switch(i.type) {
default: // To quiet the compiler
case 0:
return new Aluminum(i.data);
case 1:
return new Paper(i.data);
case 2:
return new Glass(i.data);
// Two lines here:
case 3:
return new Cardboard(i.data);
}
} for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++)
bin.addElement(
Trash.factory(
new Info(
(int)(Math.random() * Info.MAX_NUM),
Math.random() * 100)));//: Trash.java
// Base class for Trash recycling examples
package c16.trash;
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
public abstract class Trash {
private double weight;
Trash(double wt) { weight = wt; }
Trash() {}
public abstract double value();
public double weight() { return weight; }
// Sums the value of Trash in a bin:
public static void sumValue(Vector bin) {
Enumeration e = bin.elements();
double val = 0.0f;
while(e.hasMoreElements()) {
// One kind of RTTI:
// A dynamically-checked cast
Trash t = (Trash)e.nextElement();
val += t.weight() * t.value();
System.out.println(
"weight of " +
// Using RTTI to get type
// information about the class:
t.getClass().getName() +
" = " + t.weight());
}
System.out.println("Total value = " + val);
}
// Remainder of class provides support for
// prototyping:
public static class PrototypeNotFoundException
extends Exception {}
public static class CannotCreateTrashException
extends Exception {}
private static Vector trashTypes =
new Vector();
public static Trash factory(Info info)
throws PrototypeNotFoundException,
CannotCreateTrashException {
for(int i = 0; i < trashTypes.size(); i++) {
// Somehow determine the new type
// to create, and create one:
Class tc =
(Class)trashTypes.elementAt(i);
if (tc.getName().indexOf(info.id) != -1) {
try {
// Get the dynamic constructor method
// that takes a double argument:
Constructor ctor =
tc.getConstructor(
new Class[] {double.class});
// Call the constructor to create a
// new object:
return (Trash)ctor.newInstance(
new Object[]{new Double(info.data)});
} catch(Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
throw new CannotCreateTrashException();
}
}
}
// Class was not in the list. Try to load it,
// but it must be in your class path!
try {
System.out.println("Loading " + info.id);
trashTypes.addElement(
Class.forName(info.id));
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new PrototypeNotFoundException();
}
// Loaded successfully. Recursive call
// should work this time:
return factory(info);
}
public static class Info {
public String id;
public double data;
public Info(String name, double data) {
id = name;
this.data = data;
}
}
} ///:~//: Aluminum.java
// The Aluminum class with prototyping
package c16.trash;
public class Aluminum extends Trash {
private static double val = 1.67f;
public Aluminum(double wt) { super(wt); }
public double value() { return val; }
public static void value(double newVal) {
val = newVal;
}
} ///:~//: Cardboard.java
// The Cardboard class with prototyping
package c16.trash;
public class Cardboard extends Trash {
private static double val = 0.23f;
public Cardboard(double wt) { super(wt); }
public double value() { return val; }
public static void value(double newVal) {
val = newVal;
}
} ///:~c16.Trash.Glass:54 c16.Trash.Paper:22 c16.Trash.Paper:11 c16.Trash.Glass:17 c16.Trash.Aluminum:89 c16.Trash.Paper:88 c16.Trash.Aluminum:76 c16.Trash.Cardboard:96 c16.Trash.Aluminum:25 c16.Trash.Aluminum:34 c16.Trash.Glass:11 c16.Trash.Glass:68 c16.Trash.Glass:43 c16.Trash.Aluminum:27 c16.Trash.Cardboard:44 c16.Trash.Aluminum:18 c16.Trash.Paper:91 c16.Trash.Glass:63 c16.Trash.Glass:50 c16.Trash.Glass:80 c16.Trash.Aluminum:81 c16.Trash.Cardboard:12 c16.Trash.Glass:12 c16.Trash.Glass:54 c16.Trash.Aluminum:36 c16.Trash.Aluminum:93 c16.Trash.Glass:93 c16.Trash.Paper:80 c16.Trash.Glass:36 c16.Trash.Glass:12 c16.Trash.Glass:60 c16.Trash.Paper:66 c16.Trash.Aluminum:36 c16.Trash.Cardboard:22
//: ParseTrash.java
// Open a file and parse its contents into
// Trash objects, placing each into a Vector
package c16.trash;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ParseTrash {
public static void
fillBin(String filename, Fillable bin) {
try {
BufferedReader data =
new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filename));
String buf;
while((buf = data.readLine())!= null) {
String type = buf.substring(0,
buf.indexOf(':')).trim();
double weight = Double.valueOf(
buf.substring(buf.indexOf(':') + 1)
.trim()).doubleValue();
bin.addTrash(
Trash.factory(
new Trash.Info(type, weight)));
}
data.close();
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Special case to handle Vector:
public static void
fillBin(String filename, Vector bin) {
fillBin(filename, new FillableVector(bin));
}
} ///:~//: Fillable.java
// Any object that can be filled with Trash
package c16.trash;
public interface Fillable {
void addTrash(Trash t);
} ///:~//: FillableVector.java
// Adapter that makes a Vector Fillable
package c16.trash;
import java.util.*;
public class FillableVector implements Fillable {
private Vector v;
public FillableVector(Vector vv) { v = vv; }
public void addTrash(Trash t) {
v.addElement(t);
}
} ///:~ public static void
fillBin(String filename, Vector bin) {
fillBin(filename, new FillableVector(bin));
}//: RecycleAP.java
// Recycling with RTTI and Prototypes
package c16.recycleap;
import c16.trash.*;
import java.util.*;
public class RecycleAP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector bin = new Vector();
// Fill up the Trash bin:
ParseTrash.fillBin("Trash.dat", bin);
Vector
glassBin = new Vector(),
paperBin = new Vector(),
alBin = new Vector();
Enumeration sorter = bin.elements();
// Sort the Trash:
while(sorter.hasMoreElements()) {
Object t = sorter.nextElement();
// RTTI to show class membership:
if(t instanceof Aluminum)
alBin.addElement(t);
if(t instanceof Paper)
paperBin.addElement(t);
if(t instanceof Glass)
glassBin.addElement(t);
}
Trash.sumValue(alBin);
Trash.sumValue(paperBin);
Trash.sumValue(glassBin);
Trash.sumValue(bin);
}
} ///:~

//: RecycleB.java
// Adding more objects to the recycling problem
package c16.recycleb;
import c16.trash.*;
import java.util.*;
// A vector that admits only the right type:
class Tbin extends Vector {
Class binType;
Tbin(Class binType) {
this.binType = binType;
}
boolean grab(Trash t) {
// Comparing class types:
if(t.getClass().equals(binType)) {
addElement(t);
return true; // Object grabbed
}
return false; // Object not grabbed
}
}
class TbinList extends Vector { //(*1*)
boolean sort(Trash t) {
Enumeration e = elements();
while(e.hasMoreElements()) {
Tbin bin = (Tbin)e.nextElement();
if(bin.grab(t)) return true;
}
return false; // bin not found for t
}
void sortBin(Tbin bin) { // (*2*)
Enumeration e = bin.elements();
while(e.hasMoreElements())
if(!sort((Trash)e.nextElement()))
System.out.println("Bin not found");
}
}
public class RecycleB {
static Tbin bin = new Tbin(Trash.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Fill up the Trash bin:
ParseTrash.fillBin("Trash.dat", bin);
TbinList trashBins = new TbinList();
trashBins.addElement(
new Tbin(Aluminum.class));
trashBins.addElement(
new Tbin(Paper.class));
trashBins.addElement(
new Tbin(Glass.class));
// add one line here: (*3*)
trashBins.addElement(
new Tbin(Cardboard.class));
trashBins.sortBin(bin); // (*4*)
Enumeration e = trashBins.elements();
while(e.hasMoreElements()) {
Tbin b = (Tbin)e.nextElement();
Trash.sumValue(b);
}
Trash.sumValue(bin);
}
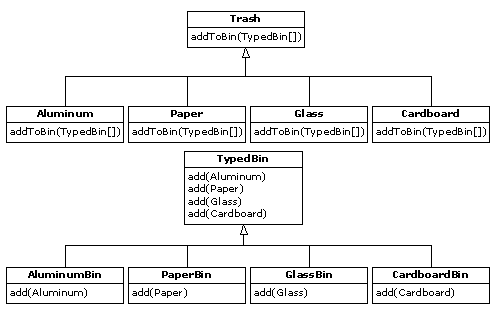
} ///:~
//: TypedBinMember.java
// An interface for adding the double dispatching
// method to the trash hierarchy without
// modifying the original hierarchy.
package c16.doubledispatch;
interface TypedBinMember {
// The new method:
boolean addToBin(TypedBin[] tb);
} ///:~//: DDAluminum.java
// Aluminum for double dispatching
package c16.doubledispatch;
import c16.trash.*;
public class DDAluminum extends Aluminum
implements TypedBinMember {
public DDAluminum(double wt) { super(wt); }
public boolean addToBin(TypedBin[] tb) {
for(int i = 0; i < tb.length; i++)
if(tb[i].add(this))
return true;
return false;
}
} ///:~//: DDPaper.java
// Paper for double dispatching
package c16.doubledispatch;
import c16.trash.*;
public class DDPaper extends Paper
implements TypedBinMember {
public DDPaper(double wt) { super(wt); }
public boolean addToBin(TypedBin[] tb) {
for(int i = 0; i < tb.length; i++)
if(tb[i].add(this))
return true;
return false;
}
} ///:~//: DDGlass.java
// Glass for double dispatching
package c16.doubledispatch;
import c16.trash.*;
public class DDGlass extends Glass
implements TypedBinMember {
public DDGlass(double wt) { super(wt); }
public boolean addToBin(TypedBin[] tb) {
for(int i = 0; i < tb.length; i++)
if(tb[i].add(this))
return true;
return false;
}
} ///:~//: DDCardboard.java
// Cardboard for double dispatching
package c16.doubledispatch;
import c16.trash.*;
public class DDCardboard extends Cardboard
implements TypedBinMember {
public DDCardboard(double wt) { super(wt); }
public boolean addToBin(TypedBin[] tb) {
for(int i = 0; i < tb.length; i++)
if(tb[i].add(this))
return true;
return false;
}
} ///:~//: TypedBin.java
// Vector that knows how to grab the right type
package c16.doubledispatch;
import c16.trash.*;
import java.util.*;
public abstract class TypedBin {
Vector v = new Vector();
protected boolean addIt(Trash t) {
v.addElement(t);
return true;
}
public Enumeration elements() {
return v.elements();
}
public boolean add(DDAluminum a) {
return false;
}
public boolean add(DDPaper a) {
return false;
}
public boolean add(DDGlass a) {
return false;
}
public boolean add(DDCardboard a) {
return false;
}
} ///:~c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:54 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDPaper:22 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDPaper:11 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:17 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:89 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDPaper:88 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:76 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDCardboard:96 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:25 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:34 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:11 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:68 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:43 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:27 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDCardboard:44 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:18 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDPaper:91 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:63 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:50 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:80 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:81 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDCardboard:12 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:12 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:54 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:36 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:93 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:93 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDPaper:80 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:36 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:12 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDGlass:60 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDPaper:66 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDAluminum:36 c16.DoubleDispatch.DDCardboard:22
//: DoubleDispatch.java
// Using multiple dispatching to handle more
// than one unknown type during a method call.
package c16.doubledispatch;
import c16.trash.*;
import java.util.*;
class AluminumBin extends TypedBin {
public boolean add(DDAluminum a) {
return addIt(a);
}
}
class PaperBin extends TypedBin {
public boolean add(DDPaper a) {
return addIt(a);
}
}
class GlassBin extends TypedBin {
public boolean add(DDGlass a) {
return addIt(a);
}
}
class CardboardBin extends TypedBin {
public boolean add(DDCardboard a) {
return addIt(a);
}
}
class TrashBinSet {
private TypedBin[] binSet = {
new AluminumBin(),
new PaperBin(),
new GlassBin(),
new CardboardBin()
};
public void sortIntoBins(Vector bin) {
Enumeration e = bin.elements();
while(e.hasMoreElements()) {
TypedBinMember t =
(TypedBinMember)e.nextElement();
if(!t.addToBin(binSet))
System.err.println("Couldn't add " + t);
}
}
public TypedBin[] binSet() { return binSet; }
}
public class DoubleDispatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector bin = new Vector();
TrashBinSet bins = new TrashBinSet();
// ParseTrash still works, without changes:
ParseTrash.fillBin("DDTrash.dat", bin);
// Sort from the master bin into the
// individually-typed bins:
bins.sortIntoBins(bin);
TypedBin[] tb = bins.binSet();
// Perform sumValue for each bin...
for(int i = 0; i < tb.length; i++)
Trash.sumValue(tb[i].v);
// ... and for the master bin
Trash.sumValue(bin);
}
} ///:~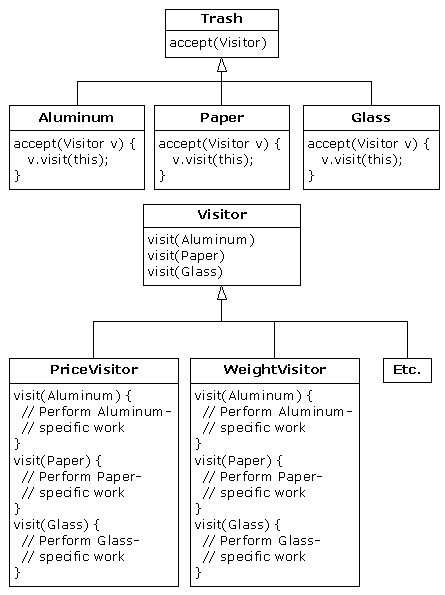
//: Visitable.java
// An interface to add visitor functionality to
// the Trash hierarchy without modifying the
// base class.
package c16.trashvisitor;
import c16.trash.*;
interface Visitable {
// The new method:
void accept(Visitor v);
} ///:~//: VAluminum.java
// Aluminum for the visitor pattern
package c16.trashvisitor;
import c16.trash.*;
public class VAluminum extends Aluminum
implements Visitable {
public VAluminum(double wt) { super(wt); }
public void accept(Visitor v) {
v.visit(this);
}
} ///:~//: VPaper.java
// Paper for the visitor pattern
package c16.trashvisitor;
import c16.trash.*;
public class VPaper extends Paper
implements Visitable {
public VPaper(double wt) { super(wt); }
public void accept(Visitor v) {
v.visit(this);
}
} ///:~//: VGlass.java
// Glass for the visitor pattern
package c16.trashvisitor;
import c16.trash.*;
public class VGlass extends Glass
implements Visitable {
public VGlass(double wt) { super(wt); }
public void accept(Visitor v) {
v.visit(this);
}
} ///:~//: VCardboard.java
// Cardboard for the visitor pattern
package c16.trashvisitor;
import c16.trash.*;
public class VCardboard extends Cardboard
implements Visitable {
public VCardboard(double wt) { super(wt); }
public void accept(Visitor v) {
v.visit(this);
}
} ///:~//: Visitor.java
// The base interface for visitors
package c16.trashvisitor;
import c16.trash.*;
interface Visitor {
void visit(VAluminum a);
void visit(VPaper p);
void visit(VGlass g);
void visit(VCardboard c);
} ///:~c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:54 c16.TrashVisitor.VPaper:22 c16.TrashVisitor.VPaper:11 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:17 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:89 c16.TrashVisitor.VPaper:88 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:76 c16.TrashVisitor.VCardboard:96 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:25 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:34 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:11 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:68 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:43 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:27 c16.TrashVisitor.VCardboard:44 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:18 c16.TrashVisitor.VPaper:91 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:63 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:50 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:80 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:81 c16.TrashVisitor.VCardboard:12 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:12 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:54 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:36 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:93 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:93 c16.TrashVisitor.VPaper:80 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:36 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:12 c16.TrashVisitor.VGlass:60 c16.TrashVisitor.VPaper:66 c16.TrashVisitor.VAluminum:36 c16.TrashVisitor.VCardboard:22
//: TrashVisitor.java
// The "visitor" pattern
package c16.trashvisitor;
import c16.trash.*;
import java.util.*;
// Specific group of algorithms packaged
// in each implementation of Visitor:
class PriceVisitor implements Visitor {
private double alSum; // Aluminum
private double pSum; // Paper
private double gSum; // Glass
private double cSum; // Cardboard
public void visit(VAluminum al) {
double v = al.weight() * al.value();
System.out.println(
"value of Aluminum= " + v);
alSum += v;
}
public void visit(VPaper p) {
double v = p.weight() * p.value();
System.out.println(
"value of Paper= " + v);
pSum += v;
}
public void visit(VGlass g) {
double v = g.weight() * g.value();
System.out.println(
"value of Glass= " + v);
gSum += v;
}
public void visit(VCardboard c) {
double v = c.weight() * c.value();
System.out.println(
"value of Cardboard = " + v);
cSum += v;
}
void total() {
System.out.println(
"Total Aluminum: $" + alSum + "\n" +
"Total Paper: $" + pSum + "\n" +
"Total Glass: $" + gSum + "\n" +
"Total Cardboard: $" + cSum);
}
}
class WeightVisitor implements Visitor {
private double alSum; // Aluminum
private double pSum; // Paper
private double gSum; // Glass
private double cSum; // Cardboard
public void visit(VAluminum al) {
alSum += al.weight();
System.out.println("weight of Aluminum = "
+ al.weight());
}
public void visit(VPaper p) {
pSum += p.weight();
System.out.println("weight of Paper = "
+ p.weight());
}
public void visit(VGlass g) {
gSum += g.weight();
System.out.println("weight of Glass = "
+ g.weight());
}
public void visit(VCardboard c) {
cSum += c.weight();
System.out.println("weight of Cardboard = "
+ c.weight());
}
void total() {
System.out.println("Total weight Aluminum:"
+ alSum);
System.out.println("Total weight Paper:"
+ pSum);
System.out.println("Total weight Glass:"
+ gSum);
System.out.println("Total weight Cardboard:"
+ cSum);
}
}
public class TrashVisitor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector bin = new Vector();
// ParseTrash still works, without changes:
ParseTrash.fillBin("VTrash.dat", bin);
// You could even iterate through
// a list of visitors!
PriceVisitor pv = new PriceVisitor();
WeightVisitor wv = new WeightVisitor();
Enumeration it = bin.elements();
while(it.hasMoreElements()) {
Visitable v = (Visitable)it.nextElement();
v.accept(pv);
v.accept(wv);
}
pv.total();
wv.total();
}
} ///:~//: DynaTrash.java
// Using a Hashtable of Vectors and RTTI
// to automatically sort trash into
// vectors. This solution, despite the
// use of RTTI, is extensible.
package c16.dynatrash;
import c16.trash.*;
import java.util.*;
// Generic TypeMap works in any situation:
class TypeMap {
private Hashtable t = new Hashtable();
public void add(Object o) {
Class type = o.getClass();
if(t.containsKey(type))
((Vector)t.get(type)).addElement(o);
else {
Vector v = new Vector();
v.addElement(o);
t.put(type,v);
}
}
public Vector get(Class type) {
return (Vector)t.get(type);
}
public Enumeration keys() { return t.keys(); }
// Returns handle to adapter class to allow
// callbacks from ParseTrash.fillBin():
public Fillable filler() {
// Anonymous inner class:
return new Fillable() {
public void addTrash(Trash t) { add(t); }
};
}
}
public class DynaTrash {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TypeMap bin = new TypeMap();
ParseTrash.fillBin("Trash.dat",bin.filler());
Enumeration keys = bin.keys();
while(keys.hasMoreElements())
Trash.sumValue(
bin.get((Class)keys.nextElement()));
}
} ///:~ Enumeration keys = bin.keys();
while(keys.hasMoreElements())
Trash.sumValue(
bin.get((Class)keys.nextElement()));![]()